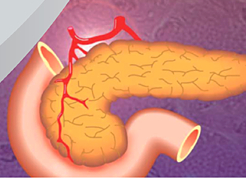
The National Institutes of Health and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation held a 3-day workshop devoted to cystic fibrosis related diabetes from June 23-25 (workshop link). The workshop was attended by interested physicians, scientists, and affected families and persons, and also was open to the public. The purpose of the workshop was to discuss the current state of knowledge about this form of diabetes, and to help inform future research directions. Dr. Larson Ode and Dr. Norris from our division both spoke on their areas of related expertise, with talks entitled “Glycemic Abnormalities in Young Children” and “Innervation of the CF Pancreas” respectively. The University of Iowa was also represented by two other speakers, gene therapy expert John Engelhardt PhD and pediatric gastroenterologist Aliye Uc MD. Drs. Engelhardt and Norris were also part of the workshop planning committee, along with other experts from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Boston Children’s Hospital.